
A femoral hernia is a bulge that forms when a part of the peritoneal sac (abdominal wall), consisting of fatty tissue, intestine or other structures, protrudes and is visible just below your lower abdomen and upper thigh, near your groin crease or labia (skin folds around the vagina).
Mr.AbhayChopada a laparoscopic general and colorectal consultant specialises in the management and treatment of different types of herniaincluding femoral hernia.As one of UK’s Top Surgical Gastroenterologists, is well known for his expertise in this field.
A hernia is a bulge that forms when the organs of the abdominal cavity push out through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. The muscles of your abdominal wall are strong and tight enough to keep the internal organs in place; but muscle weakness, previous abdominal surgery or induced pressure in the abdominal wall may result in a hernia.
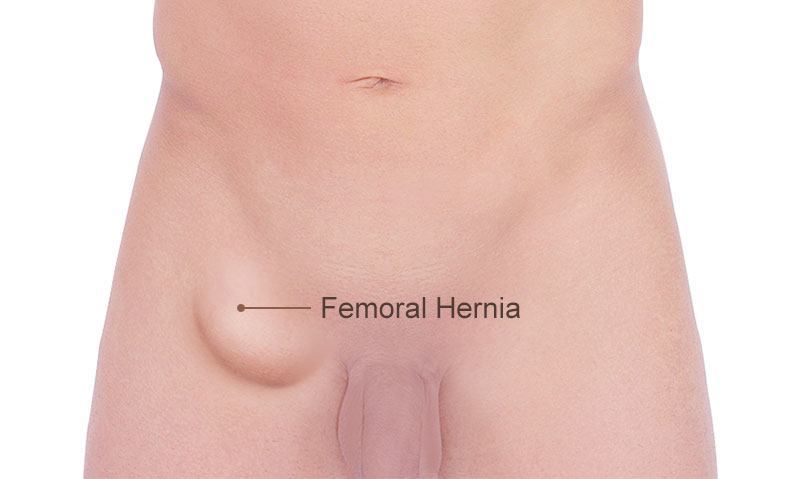
A femoral hernia is a bulge that forms when a part of the peritoneal sac (abdominal wall), consisting of fatty tissue, intestine or other structures, protrudesand is visible just below your lower abdomen and upper thigh, near your groin crease or labia (skin folds around the vagina). The bulge is pushed into your femoral canal through which your nerves and blood vessels run into the thigh region.
Femoral hernia is an uncommon type of hernia which has the probability of occurring in about one in every 20 hernias of the groin. Femoral hernia commonly occurs in women, mostly older women, because they have wider pelvises and a larger femoral canal than men. It is rarely seen in children. Femoral hernia can sometimes manifest suddenly due to abdominal pressure while straining during constipation or while you push or carry heavy objects. Obesity, pregnancy or persistent cough may also be a cause for this type of hernia.
Femoral hernia is most often mistaken for inguinal hernia, and when diagnosed, should be treated as an emergency condition.